Recent Posts
RISK DISCLOSURES ON DERIVATIVES
- 9 out of 10 individual traders in equity Futures and Options Segment, incurred net losses.
- On an average, loss makers registered net trading loss close to ₹ 50,000
- Over and above the net trading losses incurred, loss makers expended an additional 28% of net trading losses as transaction costs
- Those making net trading profits, incurred between 15% to 50% of such profits as transaction cost
Zomato-IPO

The much-awaited IPO of Zomato is finally here. The Rs. 9,375 crore public offering of Zomato comprises fresh issuance of equity shares worth Rs. 9,000 cores and an offer for sale of Rs. 375 crores from shareholders Info Edge, which is listed on exchanges. In terms of the issue size, Zomato will be the largest IPO in India since the beginning of 2021.

Company Profile - Zomato
• Zomato Limited (Zomato) is an Indian multinational restaurant aggregator and food delivery company founded by Pankaj Chaddah and Deepinder Goyal in 2008.
• Zomato provides information, menus, and user reviews of restaurants as well as food delivery options from partner restaurants in select cities.
• The company has operations in 23 countries
• Zomato generates 90% of its revenue from India.
• It is an asset-light organization, its core asset is the technology infrastructure that it has built, created, and developed over the years.
• Its platforms are used to search and discover restaurants, read and write customer-generated reviews, view and upload photos, order food delivery, book a table and make payments for delivery and while dining out at restaurants.
• It also enables its restaurant partners to buy food supplies and packaging material and enables its delivery partners to accept and service deliveries.

Open a Demat Account
Industry Outlook
• In 2015, when Zomato ventured into the food delivery business, the food delivery space was with multiple players, with around 6 players namely – Swiggy, Foodpanda, TinyOwl, Scootsy.in and OlaCafe, Uber Eats battling it out. However, over the years many of these company’s are dropped out of the race either by way of shutting down their operations or being acquired by competitors. Fast forward today, the market is now almost a duopoly – a competition between Zomato and Swiggy. However “Amazon”, which is a new entrant in the food delivery space can give a tough competition in terms of a price war with big pocket parents.
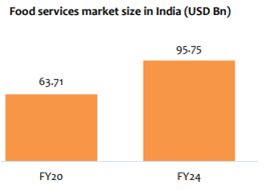
• As per a research report by USDA, the Indian foodservice market is currently valued at USD 63.71 bn and is expected to reach USD 95.75 bn by 2024. Rapid urbanization, a young population, rising disposable income, improved lifestyle, and changing consumption habits are key growth drivers of this sector. The Indian foodservice market is mainly divided into three segments – 1) dine-in, 2) takeaway and 3) food delivery. Out of these three segments, the food delivery segment is just single digit 7% of the overall business, this provides immense cushion.
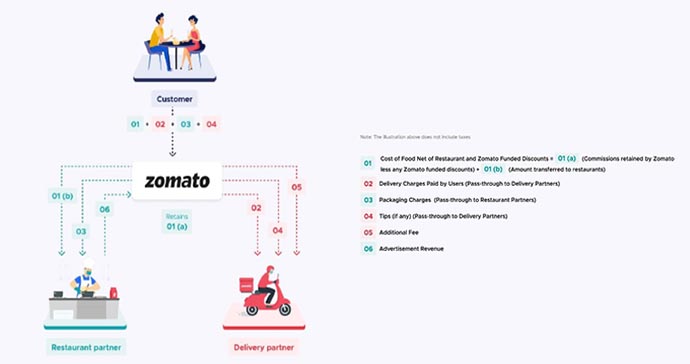
Stakeholders of Food Delivery
• Restaurant Partner Economics Zomato charges restaurant partner commissions based on an agreed-upon rate. Its remits to the restaurant partner a net amount equal to the cost of food ordered and packaging charges less the commission and any restaurant-funded discounts.
• Delivery Partner Economics Zomato remit 100% of the tips and delivery charges provided by the customer to the delivery partner (pass-through). Incrementally, It also pays the delivery partner an additional fee.
• Zomato economics It retains the commission net of any Zomato funded discounts. Additional fee to the delivery partner is paid by Zomato Company. Additionally, It also earns food delivery-related advertisement sales revenue from the restaurant.
Gross Order Value saw Sharp Reversal
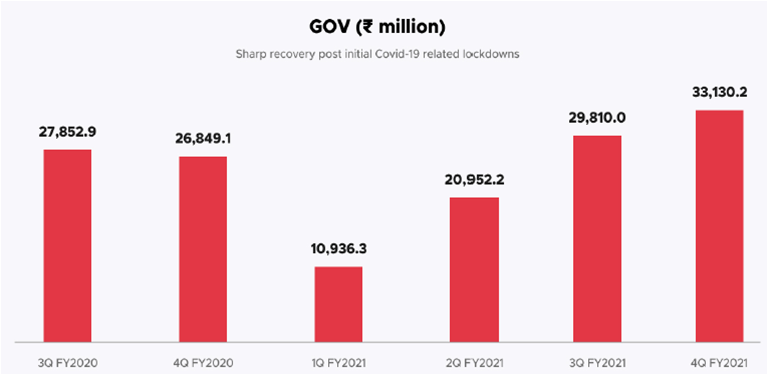
• Gross Order value of Zomato’s business saw a sharp reversal in Q4FY21 due to the opening of lockdowns and restrictions of Covid-19 second wave.
• The Q4FY21 GOV stood at Rs 3,313 Cr. Which is 23% up from Q4FY20.
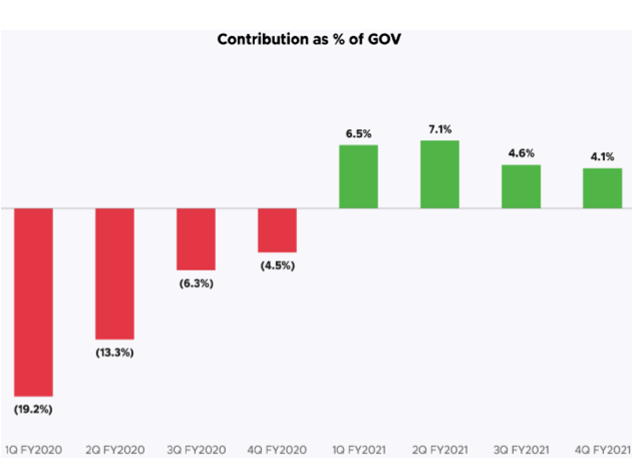
IMPROVED UNIT ECONOMICS IN FY21
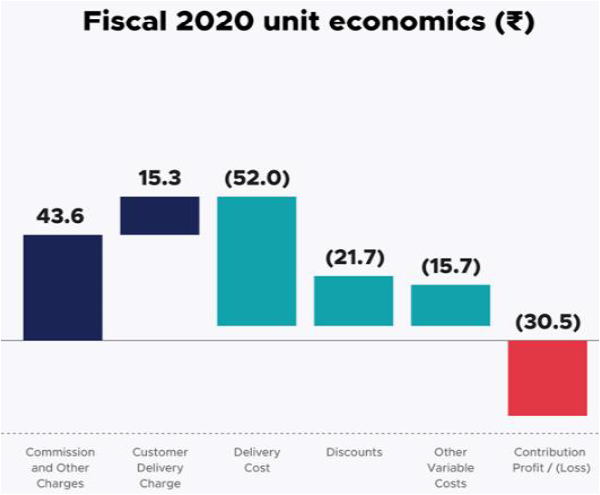
• Zomato’s business has grown rapidly since 2019, the unit economics of the food delivery business has also improved in FY 21. Company has started to show a profit in per unit.
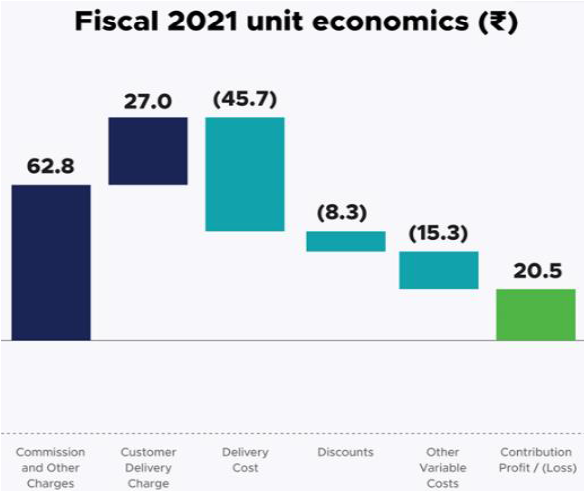
ZOMATO TURNED POSITIVE IN CONTRIBUTION
•CONTRIBUTION PROFIT: it is a sum of a) Commission and other charges b) Customer delivery charge c) Delivery cost d) Discounts e) another variable cost
•Costs associated with marketing, branding, and other fixed operating costs are excluded.
•Core business proposition has become profitable in FY21.
• The reason for the loss is the cost of fast-paced growth chased by the company.
•The cost of customer acquisition, advertising is hurting the bottom line of the company.
ONLINE FOOD DELIVERY MARKET – A LONG WAY TO GO
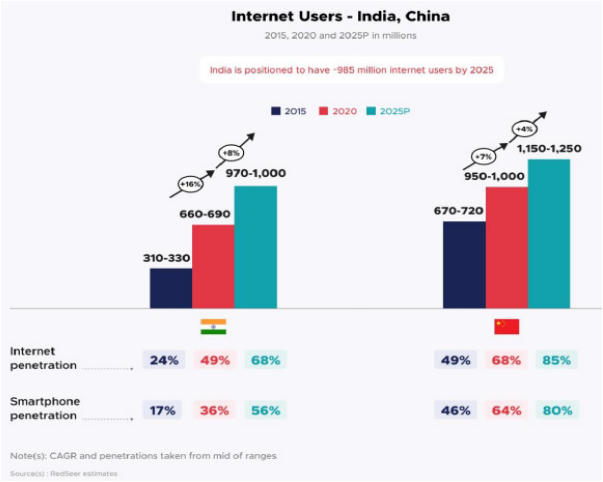
•Internet users and online food delivery penetration to improve a lot.

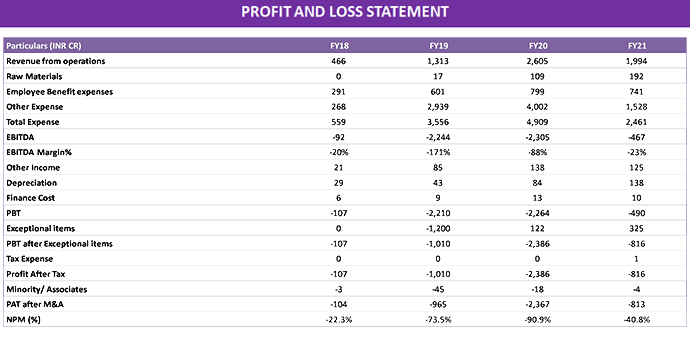
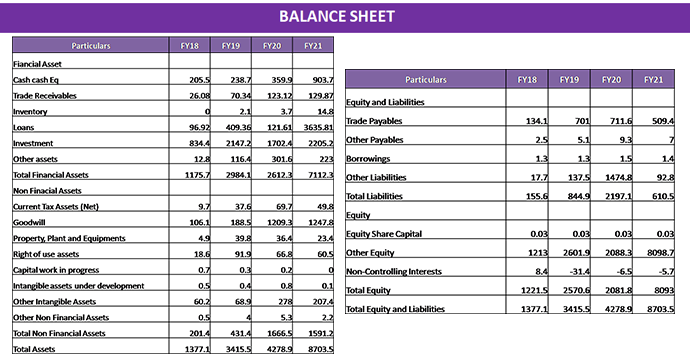
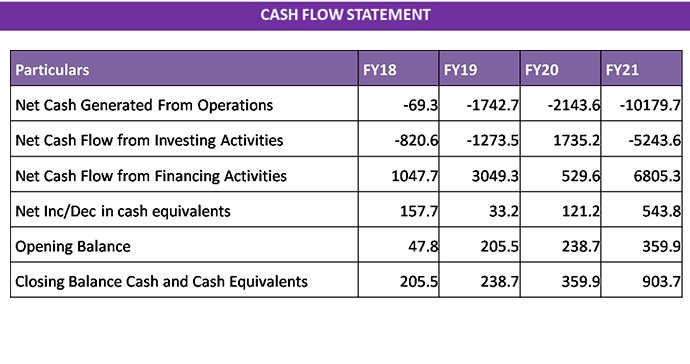
VALUATIONS
• Zomato has the first-mover advantage and it is placed well to capture the huge potential of the Online food delivery sector
• It enjoys a couple of moats and with the economics of scale started playing out, the losses have reduced substantially.
• The valuation largely comprises the future expectation of the growth from the Zomato.
• It coming with 25x FY21 EV/Sales compared to an average of 9.6x for global peers and 11.6x for Indian QSRs.
• Company has competitors which are also ready to burn cash for the price wars.
• Investors with a High-risk appetite can Subscribe for Listing Gains.

